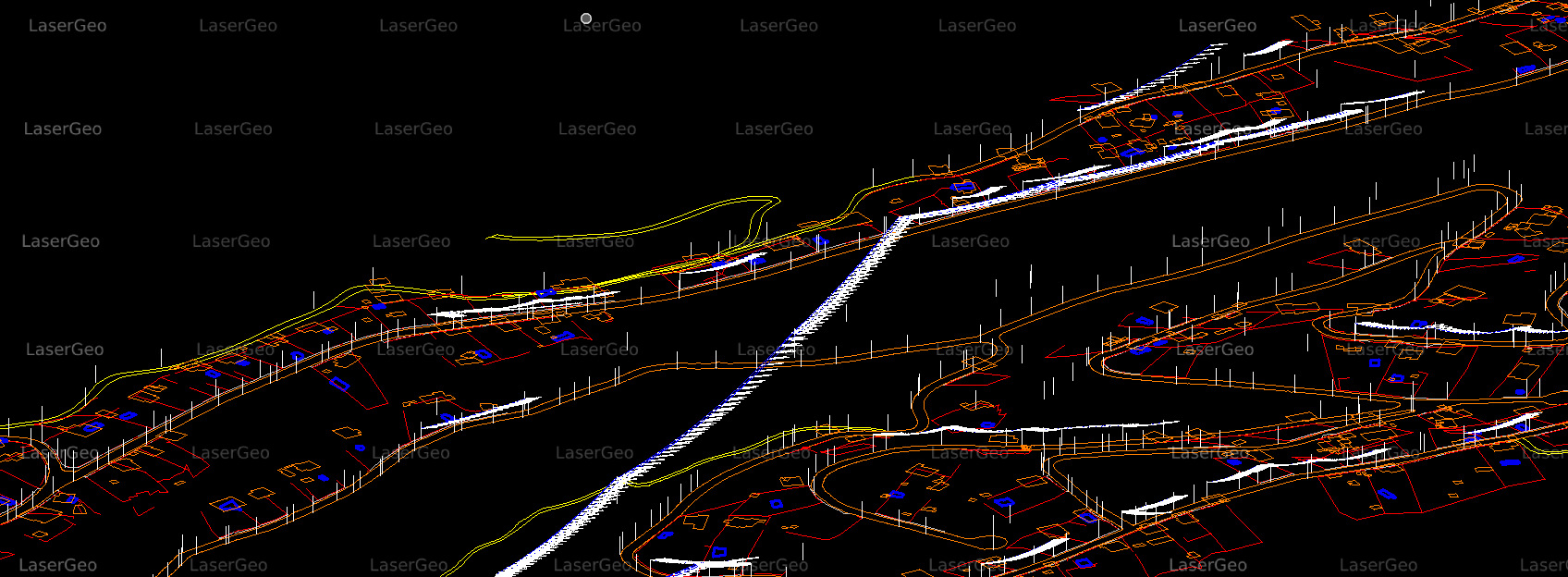
LiDAR has become an essential technology for extracting three-dimensional topographical features with unmatched precision. By emitting laser pulses and recording their return time, LiDAR gathers detailed data to create accurate 3D models of the Earth’s surface. These models incorporate both natural features, such as vegetation and terrain, and human-made structures, including buildings, roads, and other infrastructure.
The ability of LiDAR to deliver high-resolution spatial data makes it indispensable in a wide array of industries. It supports urban planners in designing smarter cities, aids construction teams in project planning, helps environmental scientists monitor ecosystems, and plays a critical role in disaster preparedness by mapping areas vulnerable to risks like floods or landslides