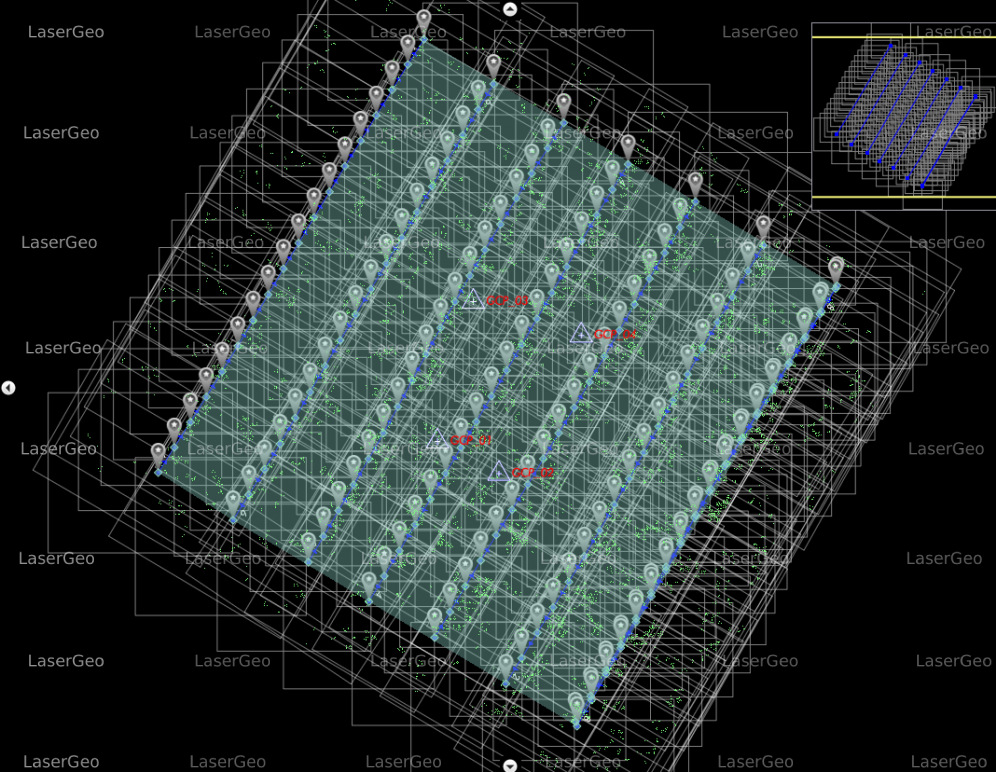
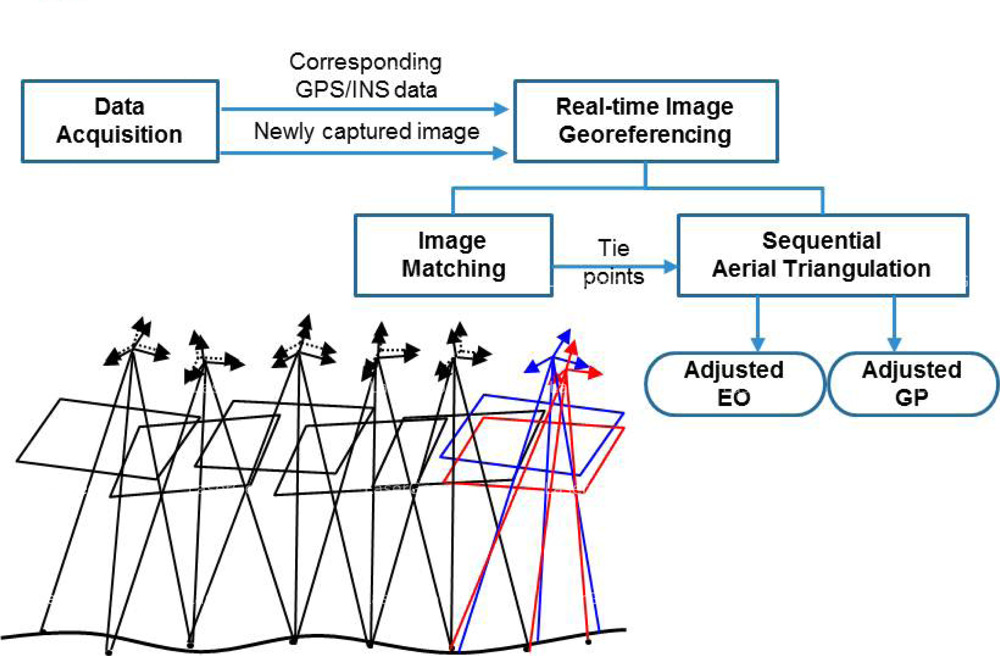
Aerial triangulation is a crucial process used to accurately determine the spatial position and orientation of individual images in a series of aerial photographs. This enables the seamless integration of these images into maps, providing a clear and detailed representation of the terrain.
The method involves calculating the x, y, and z ground coordinates of specific points by analysing measurements captured from aerial images. This ensures that all photographs align accurately, forming the foundation for subsequent photogrammetric operations.
Applications of Aerial Triangulation
The primary purpose of aerial triangulation is to extend ground control points across strips or blocks of photographs. This extension forms the basis for mapping and other geospatial analyses. By establishing precise control, aerial triangulation ensures accuracy in operations like topographic mapping, land-use analysis, and urban development projects.
Ensuring Quality in Aerial Triangulation
To maintain the accuracy and reliability of aerial triangulation results, strict quality control measures are applied throughout the process:
- Alignment Accuracy: Ensuring that relative orientations are consistent across all images within a block.
- Residual Error Minimization: Verifying that residuals from triangulation adjustments remain within 1.2 times the pixel size of the imagery.
- Root Mean Square (RMS) Values: Confirming RMS values are under 0.8 times the pixel size.
- Ground Control Point Precision: Guaranteeing that RMS values for Ground Control Points (GCPs) align with the final Ground Sample Distance (GSD) of the photographic block.