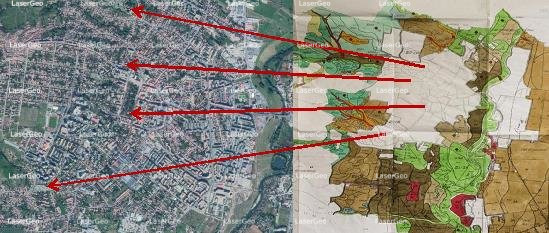
Georeferencing refers to the process of aligning spatial data—like maps, aerial images, or scanned documents—with real-world locations by applying a specific coordinate system. This alignment ensures that the data corresponds accurately to its geographical position on the Earth’s surface, making it ready for practical use in Geographic Information Systems (GIS).
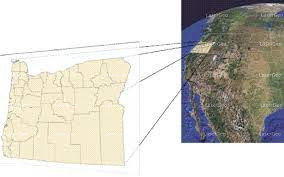
How Does Georeferencing Work?
The georeferencing process involves assigning geographic coordinates to specific features within the spatial data. These coordinates allow the data to be transformed and integrated into a common reference framework. A key aspect of georeferencing is the use of control points—well-recognized landmarks with known coordinates—that serve as anchors for positioning and transforming the dataset to align with the desired coordinate system.
Georeferencing Essential
Georeferencing is a cornerstone of geospatial analysis, enabling seamless integration of multiple datasets from various sources. By ensuring data alignment, it facilitates accurate comparative studies and supports informed decision-making. Some prominent applications of georeferencing include:
- Urban Planning: Developing accurate layouts for city infrastructure and zoning projects.
- Environmental Studies: Monitoring ecosystems and tracking changes over time.
- Navigation Systems: Enhancing the precision of location-based services and travel maps.