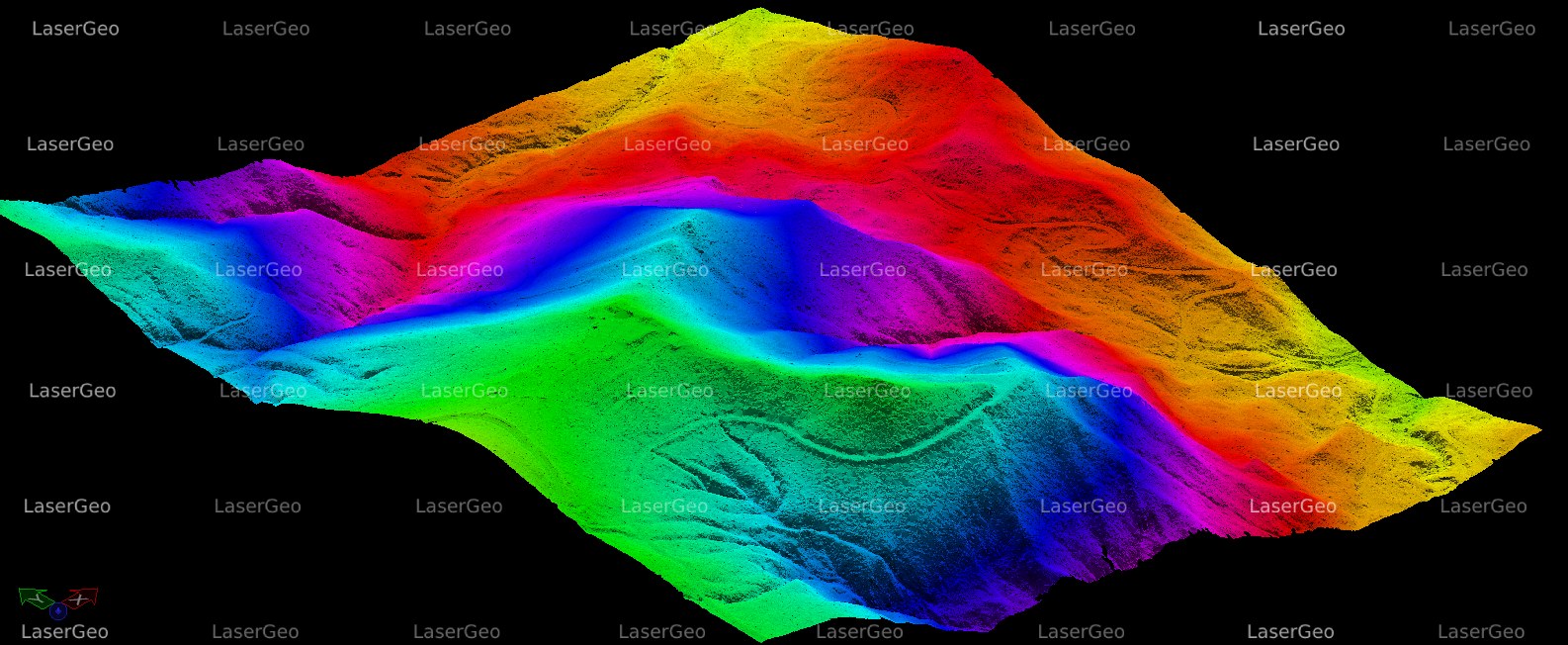
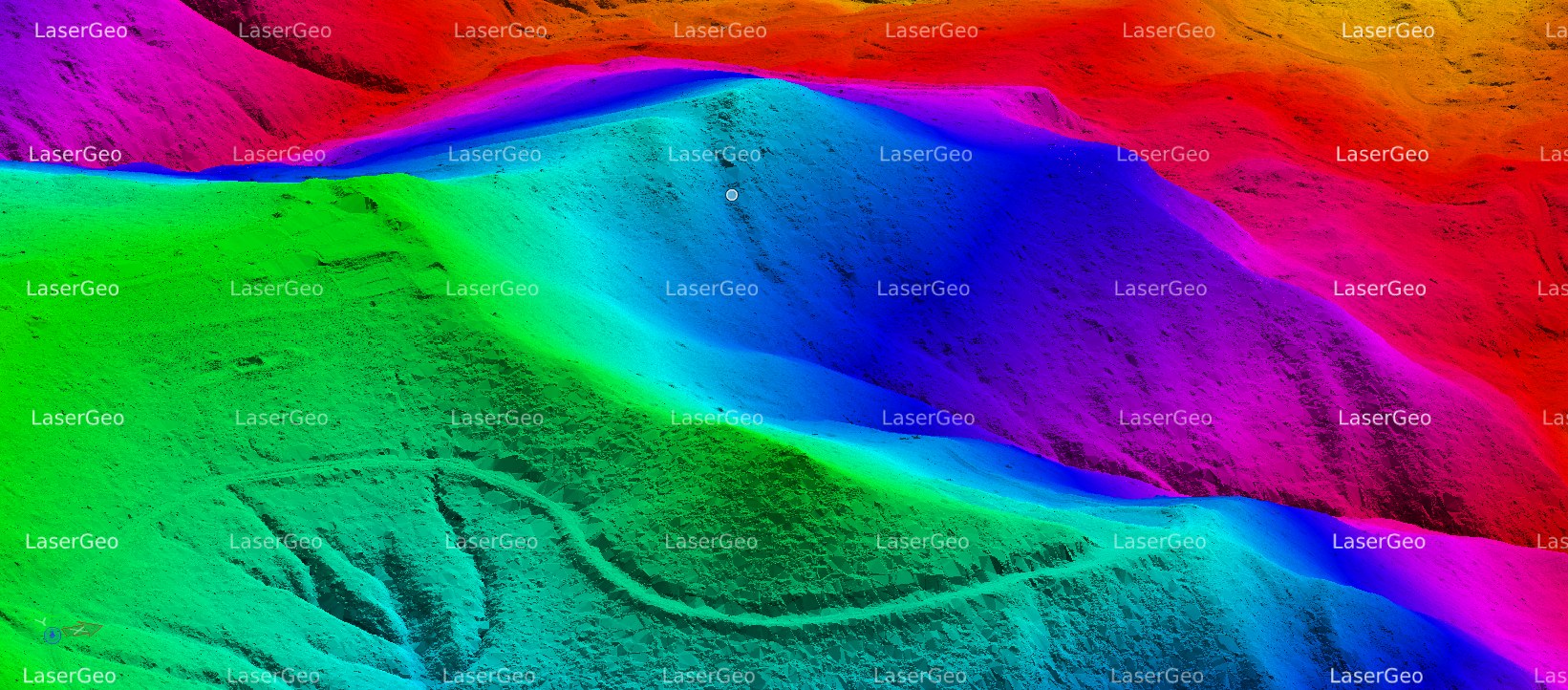
Bare Earth refers to land surfaces that are completely free from vegetation, buildings, or any other obstructions. This classification is crucial for a wide range of geospatial and environmental initiatives. By identifying and categorizing areas where the ground is exposed, we can leverage advanced remote sensing technologies like LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and satellite imagery. Accurately delineating Bare Earth allows us to gather precise elevation data, which is essential for developing complex terrain models and conducting various analyses.
The primary goal of employing Bare Ground is to support various applications that require precise terrain data. These include:
- Developing thematic maps or grid contours.
- Producing physical raised-relief maps for educational and professional purposes.
- Modelling natural phenomena like water flow, avalanches, or landslides.
- Conducting geological studies and land-use planning.
- Generating 3D Triangular Irregular Networks (TINs) for spatial analysis.
- Designing transportation systems and infrastructure.